廖龙辉
研究中心综合办公室主任
助理教授
硕士生导师
学历:博士
毕业院校:新加坡国立大学
主要研究方向:智能建造技术开发与管理、人因工程、韧性城市与基础设施
个人简介:
中共党员,硕士生导师,深圳市海外高层次人才。2018年11月加入深圳大学土木与交通工程学院、深圳大学中澳BIM与智慧建造联合研究中心。Frontiers in Built Environment期刊编辑,深圳市水务局BIM标准评审专家。主要研究方向为智能建造技术开发应用与管理、智能建造过程中的人因工程、韧性城市与基础设施等。获得各类课题10项,发表论文20余篇、专利5项。
一、近十年项目情况
1.纵向课题:
1、国家自然科学基金面上项目,参与,新型城镇化背景下城市更新的协作治理模式及优化策略研究:基于空间利益重构的视角,2022-2025,在研.
2、广东省自然科学基金面上项目,主持,基于复杂适应系统理论的建设项目BIM应用行为涌现机制研究——以粤港澳大湾区建筑业为例,2019-2022 ,在研.
3、深圳市稳定支持计划面上项目(B类),主持,融合知识本体和环境信息的深基坑开挖风险管理决策支持研究, 2022-2024,在研.
4、深圳市哲学社会科学规划青年课题, 主持,深圳建设项目区块链技术采纳行为意向的影响机制及管理策略研究, 2021-2023,在研.
2.横向课题
1、广州市建筑集团有限公司,广州国际金融城超大规模地下空间防灾减灾智慧集成关键技术及应用示范,2021-2023,在研.
二、代表性论文发表情况
研究方向一:智能建造技术开发应用与管理
[1] Xue, X., Sun, X., Xue, W., Wang, Y., & Liao, L.* (2022). Investigating building information modeling acceptance in the Chinese AECO industry. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, in press.
[2] Liao, L., Teo, E.A.L., Li, L., Zhao, X., & Wu, G. (2021). Reducing non-value adding BIM implementation activities for building projects in Singapore: Leading causes. Journal of Management in Engineering, 37(3), 05021003.
[3] Liao, L., Teo, E.A.L., Chang, R., & Zhao, X. (2020). Diffusion of building information modeling in building projects and firms in Singapore. Sustainability, 12(18), 7762.
[4] Liao, L., Teo, E.A.L, & Low, S.P. (2020). Assessing building information modeling implementation readiness in building projects in Singapore: a fuzzy synthetic evaluation approach. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 27(3), 700-724.
[5] Liao, L., Teo, E.A.L., & Chang, R. (2019). Reducing critical hindrances to building information modeling implementation: the case of the Singapore construction industry. Applied Sciences, 9(18), 3833.
[6] Ding, Z., Liu, S., Liao, L.*, & Zhang, L. (2019). A digital construction framework integrating building information modeling and reverse engineering technologies for renovation projects. Automation in Construction, 102, 45-58.
[7] Liao, L., & Teo, E.A.L. (2018). Organizational change perspective on people management in BIM implementation in building projects. Journal of Management in Engineering, 34(3), 04018008.
[8] Liao, L.*, & Teo, E.A.L. (2017). Critical success factors for enhancing the building information modelling implementation in building projects in Singapore. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 23(8), 1029-1044.
研究方向二:韧性城市与基础设施
[1] Liao, L., Quan, L., Yang, C., & Li, L. (2022). Knowledge synthesis of intelligent decision techniques applications in the AECO industry. Automation in Construction, 140, 104304.
[2] Pan, H., Yang, C.*, Quan, L., & Liao, L. (2021). A new insight into understanding urban vitality: a case study in the Chengdu-Chongqing area twin-city economic circle, China. Sustainability, 13(18), 10068.
[3] Lu, Y., Sood, T., Chang, R.*, & Liao, L. (2022). Factors impacting integrated design process of net zero energy buildings: an integrated framework. International Journal of Construction Management, 22(9), 1700-1712.
[4] Qiu, Z., Wang, Jhot and humid climates using data mining techniques. Building and Environment, 196, 107566.
[5] Quan, L., Yang, C., & Liao, L.* (2021). A review of research on supply chain resilience in the construction industry. In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate.
[6] Liang, Y., Quan, L., Yang, C., & Liao, L.* (2021). A critical review of interaction design between smart home devices and the elderly. In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate.
[7] Liao, K., Yang, C., Quan, L., & Liao, L.* (2021). Review of ergonomics application on HSE management research for construction workers. In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate.
[8] Ding, Z., Liu, S., Luo, L., & Liao, L.* (2020). A building information modeling-based carbon emission measurement system for prefabricated residential buildings during the materialization phase. Journal of Cleaner Production, 264, 121728.
三、代表性专利情况
研究方向一:智能建造技术开发应用与管理
1、基于信号采集装置的安全帽及疲劳监控系统, ZL202120543058.6; 发明人: 廖龙辉, 廖奎安, 梁逸飞, 全丽蓉, 杨川.
研究方向二:韧性城市与基础设施
1、基于联邦学习的地铁基坑开挖风险识别方法及装置, ZL202111319605.3; 发明人: 廖龙辉, 杨川, 全丽蓉, 廖奎安, 梁逸飞.
2、地下空间深基坑开挖风险监测的轻量可视化系统及方法, ZL202210186168.0; 发明人: 廖龙辉, 杨川, 全丽蓉, 廖奎安, 梁逸飞.
3、一种可拆卸家电控制装置, ZL202221506679.8; 发明人: 廖龙辉, 梁逸飞, 全丽蓉, 廖奎安, 杨川.
4、一种地铁深大基坑风险因素智能感知系统, ZL202120460836.5;发明人: 廖龙辉, 杨川, 梁逸飞, 廖奎安, 全丽蓉.
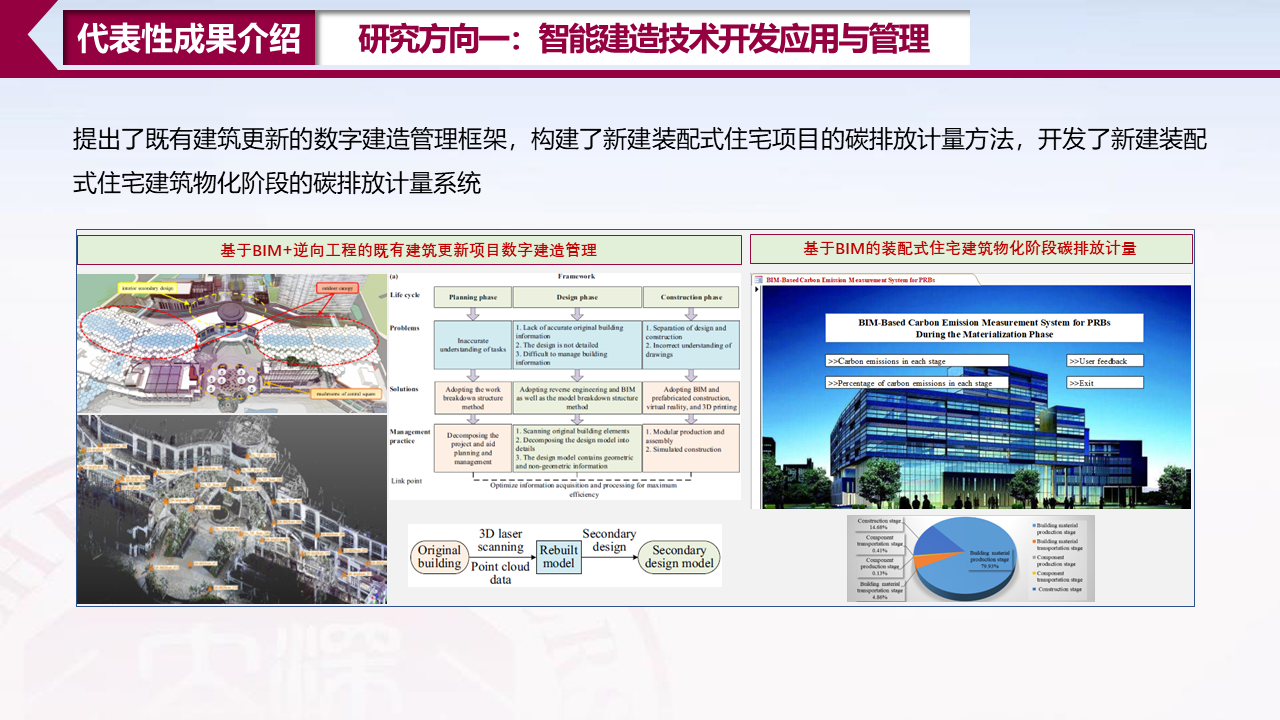
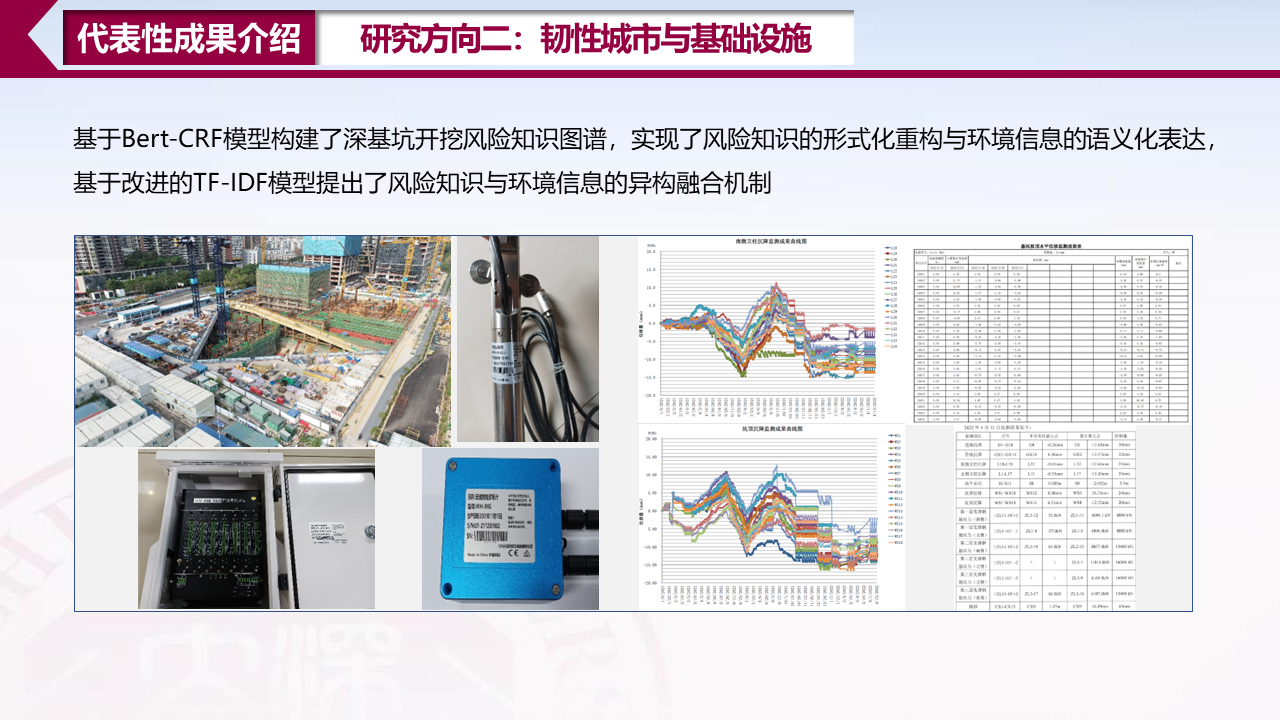
四、代表性成果介绍