吴环宇
研究中心信息与国际化办公室主任
助理教授
硕士生导师、博士后联培导师
深圳市海外高层次孔雀计划人才
中国建筑学会会员
学历:博士
毕业院校:阿德莱德大学
主要研究方向:建筑废弃物管理,复杂工程碳排放评估,建筑信息化与机器人
个人简介:
深圳市海外高层次人才、The Terence Williamson Prize in Architecture获得者。博士毕业于澳大利亚阿德莱德大学,现任深圳大学土木与交通工程学院助理教授、中澳BIM与智慧建造联合研究中心信息与国际化办公室主任、《建筑废弃物资源化与管理》公众号执行主编。主要研究方向有可持续建设、智能建造机器人、工程造价。担任《Journal of Cleaner Production》、《Resource, Conservation and Recycling》、《Frontiers of Engineering Management》、《International Journal of Construction Management》、《Journal of Green Building》等期刊审稿人。从2012年开始开展建筑废弃物管理相关研究,构建了一系列从项目、城市和国家尺度估算和预测建筑废弃物产生量与资源化潜力的模型和方法,采用LCA等方法评价建筑废弃物处理处置系统的经济、社会、环境影响。在学术期刊和国际会议上发表论文三十余篇。
一、近十年项目情况
1.纵向课题
[1] 广东省自然科学基金-面上项目,主持,基于人工智能的建筑废弃物固定消纳场安全风险评估研究,2022- 2024,在研.
[2] 深圳市海外高层次人才科研启动项目,主持,无人化建造及智能管控关键技术研究,2022- 2023,在研.
[3] 深圳大学青年教师科研启动项目,主持,粤港澳大湾区建筑废弃物跨区域处置影响,结题.
[4] 深科技创新面上项目,主持,粤港澳大湾区桥隧复杂工程碳排放评估研究,2022-2024 ,在研.
[5] 深圳大学教学改革研究项目,在研,工程造价新型创新创业人才培养研究,2021- 2022,在研.
2.横向课题
[1] 深圳市新产业投资咨询有限公司,国家优质工程管理实践与探索,在研,主持.
[2] 深圳市建筑废弃物资源化协会,深圳市建筑废弃物综合利用现状调研及政策建议研究,在研,主持.
[3] 中建一局集团第五建筑有限公司,建筑工程施工项目建筑废弃物减量与减排技术研究,在研,主持.
二、代表性论文发表情况
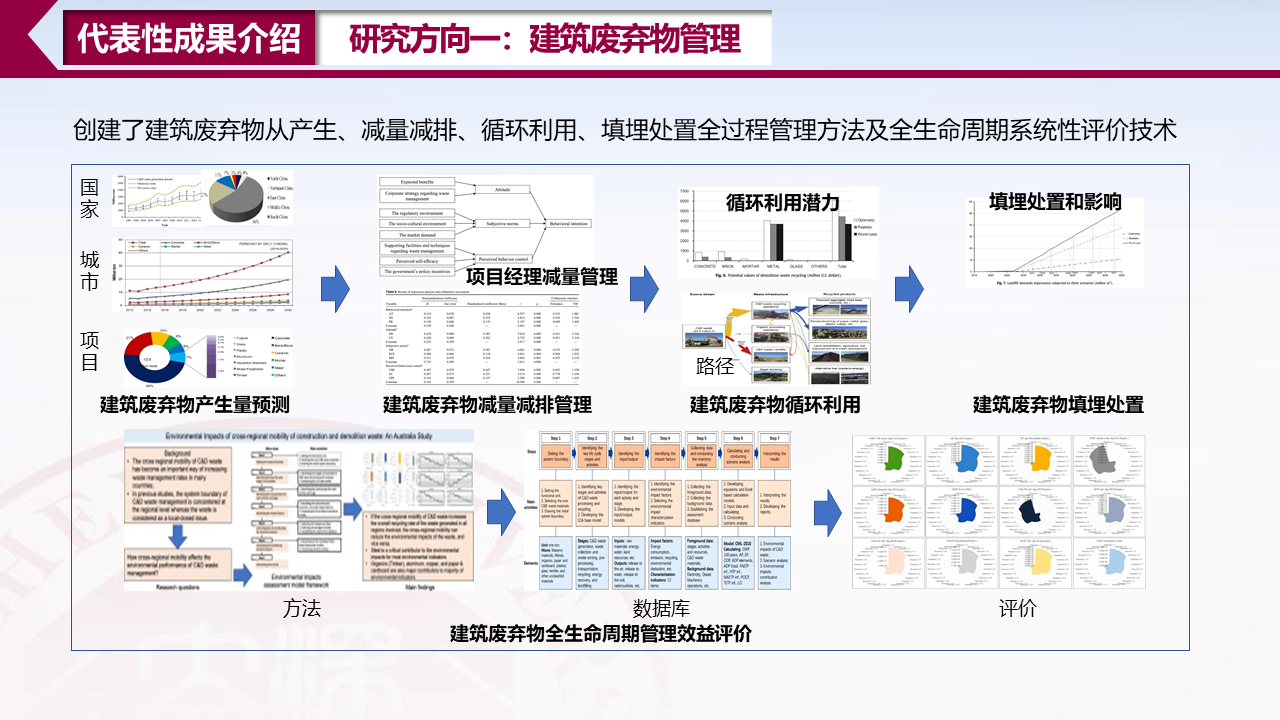
研究方向一:建筑废弃物管理
[1] Wu, H., Wang, J., Duan, H., Ouyang, L., Huang, W., & Zuo, J. (2016). An innovative approach to managing demolition waste via GIS (geographic information system): a case study in Shenzhen city, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 494-503.
[2] Wu, H., Duan, H., Zheng, L., Wang, J., Niu, Y., & Zhang, G. (2016). Demolition waste generation and recycling potentials in a rapidly developing flagship megacity of South China: Prospective scenarios and implications. Construction and Building Materials, 113, 1007-1016.
[3] Zheng, L., Wu, H., Zhang, H., Duan, H., Wang, J., Jiang, W., ... & Song, Q. (2017). Characterizing the generation and flows of construction and demolition waste in China. Construction and Building Materials, 136, 405-413.
[4] Yuan, H., Wu, H., & Zuo, J. (2018). Understanding factors influencing project managers’ behavioral intentions to reduce waste in construction projects. Journal of Management in Engineering, 34(6), 04018031.
[5] Wu, H., Zuo, J., Zillante, G., Wang, J., & Yuan, H. (2019). Construction and demolition waste research: a bibliometric analysis. Architectural Science Review, 62(4), 354-365.
[6] Wu, H., Zuo, J., Yuan, H., Zillante, G., & Wang, J. (2019). A review of performance assessment methods for construction and demolition waste management. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 150, 104407.
[7] Wu, H., Zuo, J., Zillante, G., Wang, J., & Yuan, H. (2019). Status quo and future directions of construction and demolition waste research: A critical review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 240, 118163.
[8] Wu, H., Zuo, J., Yuan, H., Zillante, G., & Wang, J. (2020). Cross-regional mobility of construction and demolition waste in Australia: An exploratory study. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 156, 104710.
[9] Ding, Z., Zhu, M., Wu, H.*, & Zuo, J. (2020). Information system with multiple data layer approach to select the C&D waste landfilling infrastructure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(31), 38788-38804.
[10] He, L., Yuan, H., & Wu, H.* (2022). Collaborative mechanism for promoting the cross-regional management of construction and demolition waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 372, 133706.
[11] Yu, B., Wang, J., Wu, H., Wong, A. B., Liao, Y., & Zuo, J. (2021). Self-fulfillment degree of construction and demolition waste management capability based on the Triple-balance theory: A case study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Waste Management, 133, 99-109.
[12] Wu, H., Zuo, J., Zillante, G., Wang, J., & Duan, H. (2021). Environmental impacts of cross-regional mobility of construction and demolition waste: An Australia Study. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 174, 105805.
[13] Ding, Z., Cao, X., Wang, Y., Wu, H.*, Zuo, J., & Zillante, G. (2022). Cost-benefit analysis of demolition waste management via agent-based modelling: A case study in Shenzhen. Waste Management, 137, 169-178.
[14] Hu, Z., Wu, G., Wu, H., & Zhang, L. (2022). Cross-sectoral preparedness and mitigation for networked typhoon disasters with cascading effects. Urban Climate, 42, 101140.
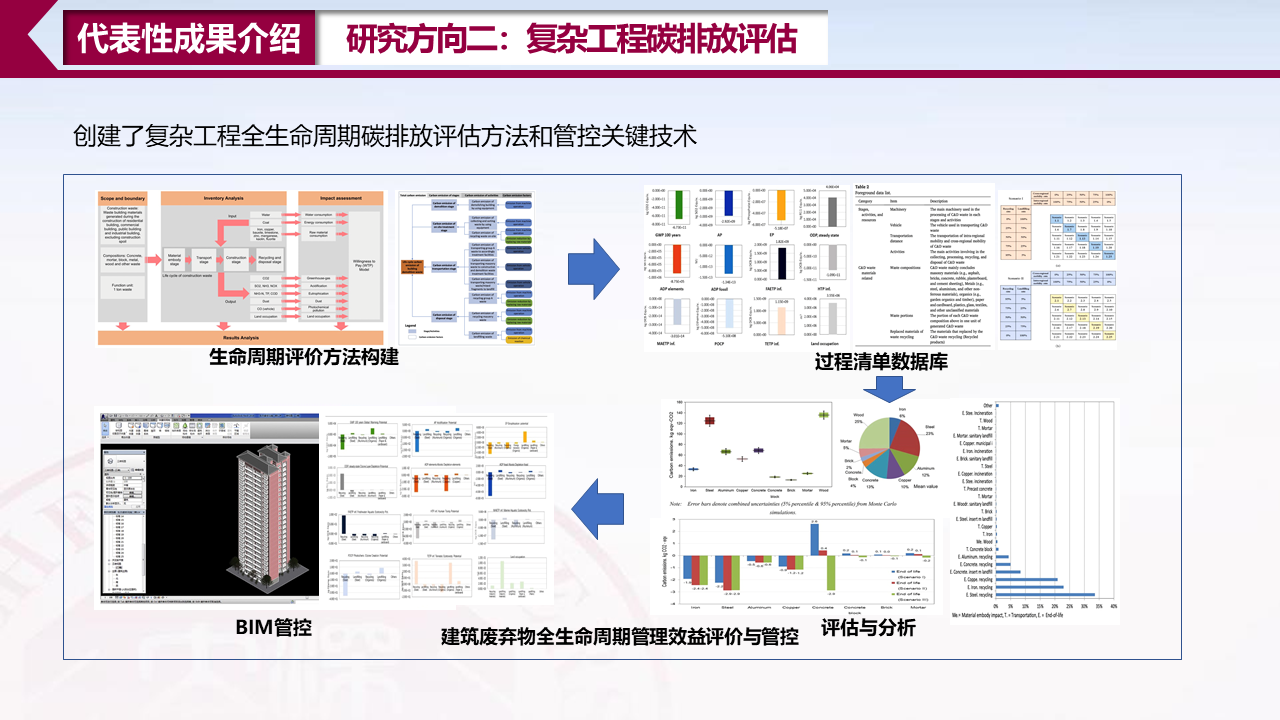
研究方向二:复杂工程碳排放评估
[1] Wu, H., Duan, H., Wang, J., Wang, T., & Wang, X. (2015). Quantification of carbon emission of construction waste by using streamlined LCA: a case study of Shenzhen, China. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 17(4), 637-645.
[2] Li, S., Wu, H., & Ding, Z. (2018). Identifying sustainable wood sources for the construction industry: a case study. Sustainability, 10(1), 139.
[3] Wang, J., Wu, H.*, Duan, H., Zillante, G., Zuo, J., & Yuan, H. (2018). Combining life cycle assessment and Building Information Modelling to account for carbon emission of building demolition waste: A case study. Journal of cleaner production, 172, 3154-3166.
[4] Wang, J., Wu, H., Tam, V. W., & Zuo, J. (2019). Considering life-cycle environmental impacts and society's willingness for optimizing construction and demolition waste management fee: An empirical study of China. Journal of cleaner production, 206, 1004-1014.
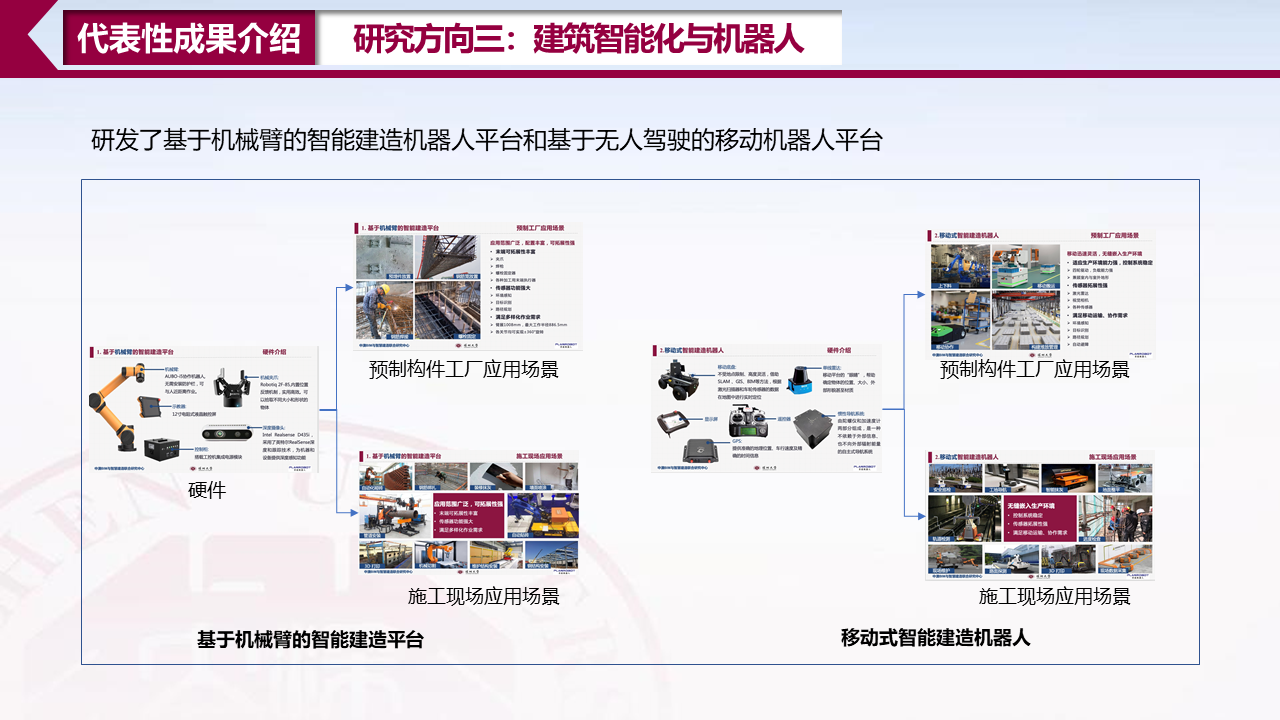
研究方向三:建筑智能化与机器人
[1] Ding, Z., Niu, J., Liu, S., Wu, H.*, & Zuo, J. (2020). An approach integrating geographic information system and building information modelling to assess the building health of commercial buildings. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120532.
[2] Lin, K., Zhou, T., Gao, X., Li, Z., Duan, H., Wu, H., ... & Zhao, Y. (2022). Deep convolutional neural networks for construction and demolition waste classification: VGGNet structures, cyclical learning rate, and knowledge transfer. Journal of Environmental Management, 318, 115501.
[3] 刘泳奇,吴环宇,陈珂. (2022).智能建造技术在工程造价管理中的应用研究综述.建筑经济, 43(87), 245-252.
三、代表性成果介绍